Introduction
As mobile app developers—especially those new to the field—it’s essential to understand that every line of code you write can influence user trust. Mobile apps handle an ever-growing share of personal and financial data, making mobile app security more critical than ever. In 2025, risks often stem from careless storage, weak authentication, or outdated dependencies. Whether you’re building a banking app or a social tool, ignoring security isn’t an option. Learning the most common risks early and applying proactive safeguards will protect users, build confidence, and prevent costly mistakes down the line.
What Is Mobile App Security & Why It Matters
Mobile application security is all about protecting apps from threats, breaches, and unauthorized access. For developers, this means going beyond writing functional code—every feature must be designed and delivered with security in mind.
Protecting User Data
With billions relying on apps for banking, shopping, and communication, even a small vulnerability can lead to major data leaks. Securing data means protecting it at every step—whether stored locally or transmitted over networks.
Maintaining Privacy & Compliance
Privacy regulations (like GDPR) require apps to safeguard user information. Failing to comply can result in penalties and reputational damage. A secure app not only meets compliance requirements but also shows users that their data is respected.
Building User Trust Through Security
Trust drives user retention. An app with robust security measures encourages users to engage confidently. Features like encryption, secure coding techniques, and regular security testing are critical to establishing this trust.
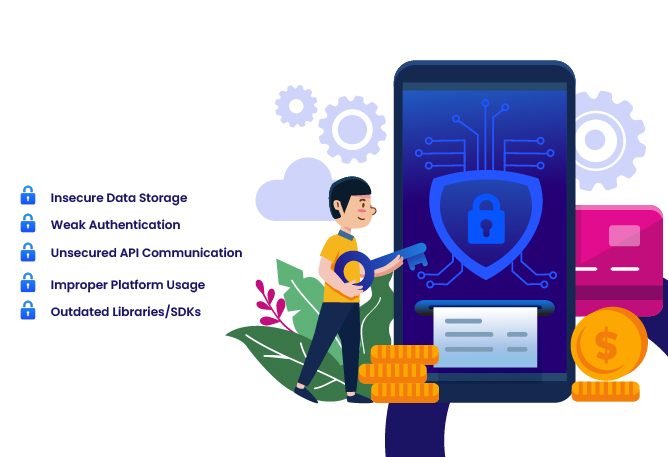
Most Common Mobile App Security Risks
Understanding where apps typically fail helps developers avoid repeating the same mistakes. Below are the most frequent risks and how to address them:
1. Insecure Data Storage
Storing sensitive data without proper safeguards makes it easy for attackers to steal or tamper with it.
-
Encrypt data before saving it locally
-
Avoid storing unnecessary personal or financial details
-
Use platform-provided secure storage options
2. Weak Authentication
Poor login systems allow attackers to bypass protections.
-
Enforce strong password policies
-
Use multi-factor authentication
-
Secure session tokens and validate them regularly
3. Unsecured API Communication
Unencrypted or unvalidated data transfer is an easy target.
-
Use HTTPS/TLS for all data communication
-
Validate inputs and outputs carefully
-
Add rate limiting to prevent brute-force attacks
4. Improper Platform Usage
Requesting excessive permissions or misusing APIs creates unnecessary exposure.
-
Request only the permissions you need
-
Follow platform security guidelines
-
Reassess permissions with every app update
5. Outdated Libraries & SDKs
Old third-party code can contain known vulnerabilities.
-
Keep all libraries and SDKs up to date
-
Monitor vulnerability reports for dependencies
-
Replace unsupported or insecure packages
Why These Risks Persist
Even in 2025, these risks continue to appear for several reasons:
Rapid Release Cycles
The rush to launch apps often leads to skipped security checks.
-
Include security reviews in every sprint
-
Avoid sacrificing security for speed
-
Educate stakeholders about long-term risks
Persistent Vulnerabilities
Some apps ship with known issues because patches are delayed.
-
Scan codebases regularly
-
Apply patches promptly
-
Maintain a vulnerability management process
Third-Party Dependency Risks
External libraries can expand your attack surface.
-
Audit all libraries before use
-
Remove unused or outdated packages
-
Track updates with automated tools
Growth of Phishing & Social Engineering
Attackers now exploit people as much as code.
-
Warn users about suspicious activity
-
Notify them of unusual login attempts
-
Educate them on safe practices
Easily Accessible Attack Tools
Reverse-engineering tools make attacks easier.
-
Obfuscate code to slow attackers
-
Implement tamper detection
-
Monitor for clones and suspicious activity
Security Best Practices for 2025
To stay ahead of threats, developers must embed security throughout the app lifecycle:
Encrypt Everything
-
Encrypt all local data, caches, and databases
-
Use AES and TLS protocols
-
Never store plain text credentials
Secure Every API
-
Require authentication/authorization for every API call
-
Validate all inputs to block malicious payloads
-
Monitor and rate-limit traffic
Obfuscate Your Code
-
Use obfuscation tools for Android & iOS
-
Remove debug logs before release
-
Apply tamper detection
Monitor & Respond
-
Log key operations and login attempts
-
Use anomaly detection and alerting systems
-
Prepare a breach response plan
Update & Audit Dependencies
-
Follow a strict dependency update schedule
-
Run automated scans for vulnerabilities
-
Replace outdated or unsupported libraries
Harden Your App Release Process
-
Sign apps with secure certificates
-
Distribute through official app stores
-
Monitor for fake or cloned versions
Conclusion
Securing mobile apps in 2025 is not a one-time task—it’s an ongoing process. By addressing key vulnerabilities like insecure storage, weak authentication, and outdated dependencies—and by applying practices like encryption, code obfuscation, and continuous monitoring—you can build resilient, trustworthy apps. Start with a security-first mindset, integrate protections at every stage of development, and keep monitoring after launch to stay ahead of evolving threats.