With the introduction of DeFi, the possibility of using blockchain technology in developing financial applications has increased. Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, has recently gained popularity as a means of raising large sums of capital for various businesses.
Lending and borrowing are two fundamental components of any financial organization. Most people will have to borrow money at some point in their lives, whether for college loans, a home, or a car.
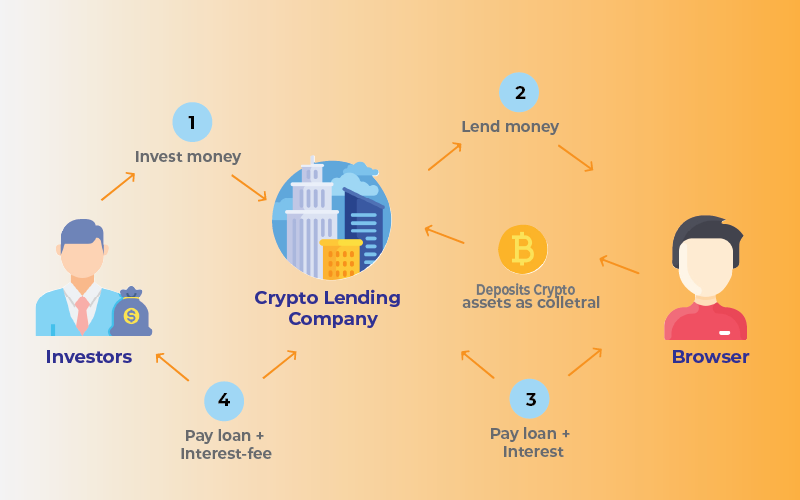
The whole lending and borrowing process is straightforward. Borrowers receive funds from lenders (also known as depositors) for a percentage of their deposits. Borrowers are also referred to as loan takers. They are willing to pay interest on the amount they receive in exchange for a lump sum payment immediately.
Historically, financial institutions such as banks have provided lending and borrowing services. They are, however, under the control of centralized systems run by government officials and gatekeepers. As a result, regular customers must deal with numerous intermediaries to obtain their funds.
And, by eliminating the need for a third party, DeFi challenges the centralized financial sector. Customers have complete control over their money with DeFi lending and borrowing, and they can become lenders or borrowers in a completely decentralized and seamless manner. It is based on open blockchains known as “smart contracts,” the most well-known of which is Ethereum.
While it is common knowledge that cryptocurrency assets fluctuate, simply holding them in wallets will not generate income. DeFi enters the picture in this case. DeFi loans help in developing money by lending your Crypto assets to borrowers. DeFi has made it possible for anyone to become a lender. As a result, you can lend your money to others and profit from the loan.
You should be familiar with two terms related to DeFi lending and borrowing. These are as follows:
Asset Collateralization in DeFi
Asset Collateralization is a fundamental concept in DeFi. The borrower guarantees an asset against which the lender can recover their capital if the borrower cannot repay the loan. When a user borrows assets from the liquidity pool, it requires some form of security or collateral. If the user fails to repay the pool’s debt, the lending protocol will not refund the collateral to the borrower; instead, it will use the assets to repay the pool’s debt.
Asset Overcollateralization in DeFi
Another critical concept in DeFi is asset over-collateralization. The borrower must deposit a Crypto asset with a higher percentage value than the assets borrowed on the DeFi platform. Borrowers should only use asset overcollateralized loans if the final investment grows faster than the debt’s interest rate. If the borrower cannot repay the loan, the borrower will become insolvent if the value of the collateralized asset falls below the total debt price.
Pros of DeFi Lending and Borrowing
- DeFi borrowing and lending are more effective at loan disbursement.
- Because DeFi protocols are open-source, they have greater transparency.
- To apply for a loan, no one’s permission is required.
- KYC procedures and data sharing are not required.
- DeFi is entirely anonymous and decentralized.
- This is an excellent way to generate passive income from your Crypto assets.
- Borrowers must over-collateralize to protect themselves against unexpected price drops.
Final Thoughts
DeFi lending and borrowing have increased dramatically in recent years. There will be new challenges in 2023, but there will also be many great opportunities. As more investors become interested in cutting-edge financial technologies, several DeFi-based initiatives are gaining traction.